
Gardeners are increasingly turning to liquid fertilizers as effective soil amendments. These fertilizers offer several advantages, such as enhanced nutrient availability and improved soil health. The global liquid fertilizers market reflects this trend, valued at approximately USD 2.63 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 3.41 billion by 2030. This growth stems from a rising demand for sustainable agricultural practices. Liquid fertilizers contribute to soil health and microbial activity, making them a smart choice for long-term gardening success.
Consider the benefits of liquid calcium, which can maintain balanced soil pH for multiple growing seasons. This prevents nutrient lock-up and ensures mineral availability, making liquid fertilizers a more sustainable option for your garden.
Key Takeaways
Liquid fertilizers enhance nutrient availability, allowing plants to access essential nutrients quickly for better growth.
Choose between organic and synthetic liquid fertilizers based on your gardening goals. Organic options improve soil health, while synthetic ones deliver nutrients rapidly.
Apply liquid fertilizers at the right time and frequency to maximize their effectiveness. Adjust your approach based on seasonal changes and plant growth stages.
Avoid common mistakes like over-application and ignoring soil testing. These practices can harm plants and the environment.
Consider using specialty liquid fertilizers for specific plant needs. They can provide targeted nutrition for improved growth and yield.
Liquid Fertilizer Benefits
Liquid fertilizers offer significant advantages for your garden, particularly in terms of nutrient availability and rapid absorption. Understanding these benefits can help you make informed decisions about your soil amendments.
Nutrient Availability
One of the primary benefits of liquid fertilizers is their ability to enhance nutrient availability in the soil. When you apply liquid fertilizers, they dissolve quickly and release essential nutrients directly into the soil. This process ensures that plants can access these nutrients more readily than with traditional granular fertilizers.
Research shows that liquid fertilizers significantly increase the availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in the soil. For example, studies indicate that all studied fertilizers lead to a marked increase in available nitrogen (AN) and available phosphorus (AP) compared to control groups. The statistical significance of these findings is noteworthy, with a p-value of less than 0.05, indicating strong evidence of effectiveness.
Fertilizer Type | Effect on Available Nitrogen (AN) | Effect on Available Phosphorus (AP) | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
All studied fertilizers | Increased significantly | Increased compared to control | p < 0.05 |
Amino acids | Source of N for plants | Chelates cations bound with phosphorus | N/A |
By improving nutrient availability, liquid fertilizers contribute to healthier plant growth and better yields. They also help maintain soil organic matter, which is crucial for long-term soil health.
Quick Absorption
Another key advantage of liquid fertilizers is their quick absorption by plant roots. Unlike granular fertilizers, which require time to break down, liquid fertilizers deliver nutrients immediately. This rapid absorption is particularly beneficial in urgent situations, such as when plants show signs of nutrient deficiencies.
Here are some reasons why liquid fertilizers excel in quick absorption:
They provide immediate availability of nutrients, promoting rapid growth and greening.
Liquid fertilizers are ideal for stimulating growth in new lawns or during critical growth phases.
They can supplement granular fertilizers effectively, ensuring that plants receive the nutrients they need without delay.
In fact, studies have shown that applying liquid fertilizers can lead to significant increases in nutrient uptake. For instance, a dose of 100 mL per pot resulted in a dramatic increase in potassium uptake, with statistical significance noted at p < 0.05.
Fertilizer Dose | N Uptake | K Uptake | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
100 mL per pot | Increased significantly | Increased dramatically | p < 0.05 |
Types of Liquid Fertilizers

When choosing liquid fertilizers, you will encounter two main categories: organic and synthetic. Understanding the differences between these options can help you make the best choice for your garden.
Organic vs. Synthetic
Organic liquid fertilizers come from natural sources, such as plant or animal materials. They improve soil health over time by adding organic matter. In contrast, synthetic liquid fertilizers are chemically manufactured. While they can deliver nutrients quickly, they may degrade soil quality and pose environmental risks.
Here’s a comparison of the two types:
Feature | Organic Liquid Fertilizer | Synthetic Liquid Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
Nutrient concentration | Lower concentrations, thus greater amounts must be used | Higher concentrations, thus smaller amounts can be used |
Consistency | The amount of nutrients varies | Defined amount of nutrients |
Nutrient release rate | The rate of nutrient release is optimal for plant uptake | Nutrients are rapidly released in quantities that may be excessive for plant uptake |
Effects on soil | Help keep the soil healthy by adding organic matter | Deleterious effects on soil microbiology and chemical structure over time |
Safety for the environment | Minimal risk of environmental pollution | High risk of leaching and greenhouse gas emissions |
Choosing between organic and synthetic fertilizers depends on your gardening goals and environmental concerns.
Specialty Formulations
Specialty liquid fertilizers target specific plant needs or deficiencies. These formulations can enhance growth and yield for particular crops. Here are some examples of specialty liquid fertilizers:
Fertilizer Type | Nutrient Composition | Specific Plant Types/Deficiencies | Effectiveness Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
Urea Ammonium Nitrate (UAN) | High Nitrogen (N) | Pastures, Crops | Significant increase in pasture productivity in dairy farming through timely applications. |
Calcium Nitrate | Nitrogen (N), Calcium | Potatoes, Tomatoes | Enhances cell structure, leading to improved yield and quality. |
Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) | High Phosphorus (P) | Horticultural Crops (Kiwifruit, Grapes) | Supports robust root systems essential for crop health. |
Potassium Nitrate | Potassium (K) | High-value Crops (Potatoes, Apples) | Improves fruit quality and disease resistance, crucial for yield maximization. |
These specialty formulations can provide targeted nutrition, ensuring your plants thrive.
Application Methods for Liquid Fertilizers

When applying liquid fertilizers, you have two primary methods: foliar feeding and soil drenching. Each method has its unique advantages and best practices. Understanding these can help you maximize the effectiveness of your liquid fertilizers.
Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding involves spraying liquid fertilizers directly onto the leaves of plants. This method allows for rapid nutrient absorption through the leaf surface. Here are some key points about foliar feeding:
Quick Nutrient Uptake: Foliar feeding provides a fast way to correct micronutrient deficiencies. Plants can absorb nutrients quickly through their leaves, leading to immediate improvements in health.
Ideal for Specific Nutrients: This method works best for micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc. These nutrients often get absorbed more efficiently through leaves than roots.
However, foliar feeding does have limitations:
Limited Nutrient Range: Not all nutrients can be effectively absorbed through leaves. Major nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus are better supplied through soil applications.
Weather Dependent: Rain can wash away the applied nutrients, reducing effectiveness. Therefore, timing your application is crucial.
Method | Nutrient Uptake Efficiency | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
Foliar Feeding | Limited but rapid | Quick correction of micronutrient deficiencies | Not all nutrients can be absorbed effectively |
Soil Drenching
Soil drenching involves applying liquid fertilizers directly to the soil around the plant’s root zone. This method ensures that nutrients reach the roots where they are needed most. Here are some benefits of soil drenching:
Comprehensive Nutrient Supply: Soil drenching provides a more balanced nutrient supply, benefiting overall plant health. It allows for the delivery of both macro and micronutrients.
Longer Lasting Effects: Nutrients applied through soil drenching can remain available for a longer period, supporting sustained plant growth.
However, soil drenching also has its challenges:
Slower Correction of Deficiencies: This method may take longer to correct acute nutrient deficiencies compared to foliar feeding.
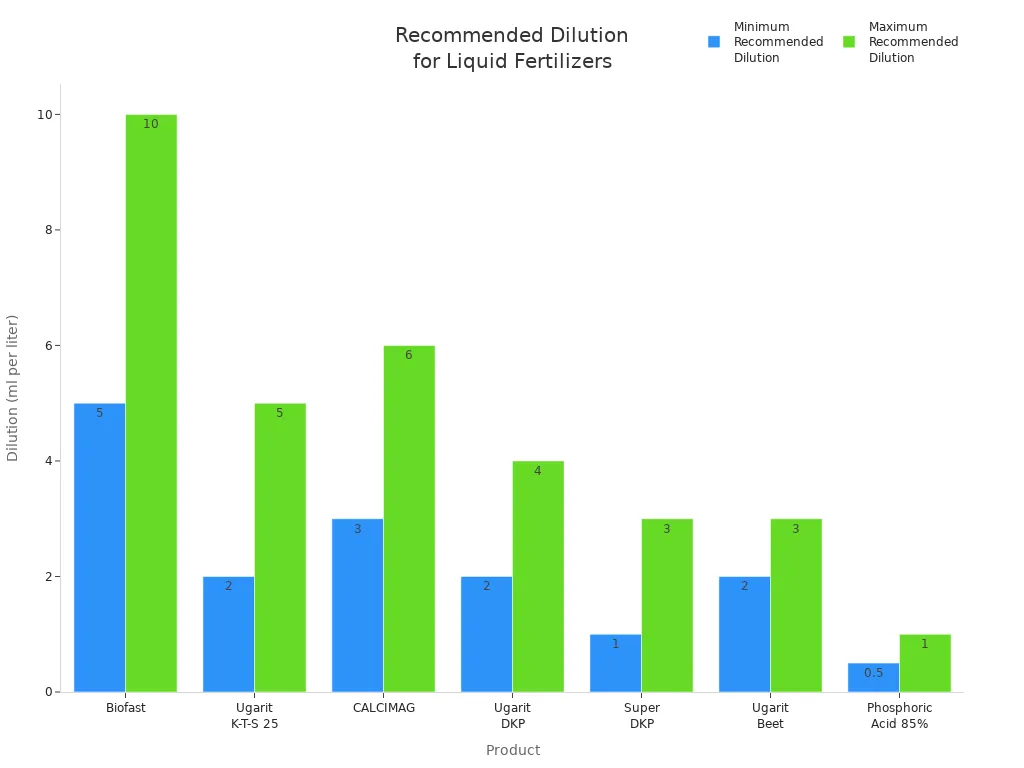
Dilution is Key: To prevent plant burn, it is essential to dilute liquid fertilizers properly. Here are some recommended dilution ratios:
Product | Application Type | Recommended Dilution |
|---|---|---|
Biofast | Foliar / Drip | 5–10 ml per liter (1:100–1:200) |
Ugarit K-T-S 25 | Drip irrigation | 2–5 ml per liter |
CALCIMAG | Calcium booster | 3–6 ml per liter |
Ugarit DKP | Flowering phase | 2–4 ml per liter |
Super DKP | Fruit filling stage | 1–3 ml per liter |
Ugarit Beet | Micronutrient mix | 2–3 ml per liter |
Phosphoric Acid 85% | pH adjustment | 0.5–1 ml per liter |
Timing and Frequency of Application
Timing and frequency play crucial roles in the effectiveness of liquid fertilizers. Understanding when to apply these fertilizers can significantly enhance plant growth and health.
Seasonal Considerations
Different seasons require different approaches to fertilization. Here’s a quick guide to help you navigate seasonal changes:
Winter: Focus on maintaining soil health. Minimal fertilization is necessary. You can add organic matter to enrich the soil.
Spring: Apply nitrogen-heavy fertilizers to support rapid growth. Monitor your plants closely to avoid over-fertilization.
Summer: Fertilize sparingly. Concentrate on heat-tolerant plants and ensure they receive adequate watering.
Fall: Balance nitrogen with phosphorus and potassium. This supports growth and root development as plants prepare for dormancy.
Growth Stages
The growth stage of your plants also dictates how often you should apply liquid fertilizers. For example, tomatoes require different application rates during their flowering and fruit maturation stages. During flowering, you might apply between 25.62 to 43.907 liters per plant, with frequencies ranging from 97 to 166 times per plant. In contrast, during fruit maturation, the rates drop to between 15.087 and 24.667 liters per plant, with application frequencies of 57 to 93 times per plant.
To help you plan your applications, here’s a table summarizing the recommended frequency for various plant types:
Plant Type | Nutrient Focus | Frequency | Example Product |
|---|---|---|---|
Lettuce, Kale | Nitrogen | Every 5–7 days | SULPHOMIN, CALCIMAG |
Tomatoes, Peppers | Phosphorus & K | Every 10–14 days | Super DKP, Ugarit Strawberry |
Grapes | Micronutrients | Monthly (foliar) | Ugarit Grapes |
Soil moisture levels also influence the absorption of liquid fertilizers. When you apply these fertilizers, nutrients dissolve quickly and move with water to the plant’s root zone. Adequate moisture is essential for effective nutrient uptake.
By considering seasonal changes and plant growth stages, you can optimize your use of liquid fertilizers for healthier plants and better yields.
Common Mistakes with Liquid Fertilizers
Over-application
Over-application of liquid fertilizers is a common mistake that can harm your plants and the environment. When you apply too much fertilizer, you risk several negative outcomes:
Root Burn: Excessive fertilizer can cause root burn, damaging the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients.
Nutrient Imbalance: Over-fertilizing creates an imbalance in soil nutrients. This imbalance can lead to poor plant health and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases.
Soil Degradation: Continuous use of synthetic fertilizers can degrade soil fertility. This degradation negatively affects the overall health of the soil ecosystem.
To avoid these issues, follow recommended timing guidelines. Apply fertilizers when your plants are actively growing. This ensures they can utilize the nutrients effectively. Remember, using the wrong type of fertilizer or applying it at the wrong time can lead to nutrient absorption problems.
Ignoring Soil Testing
Ignoring soil testing before applying liquid fertilizers is another mistake you should avoid. Soil testing helps you understand the nutrient needs of your plants. It also prevents excessive fertilizer applications that can harm the environment. Here are some key points to consider:
Optimal Nutrient Management: Soil testing allows you to determine the best crop yields and efficient use of fertilizers. This practice enhances your plants’ growth while protecting the environment.
Understanding NPK Ratios: Knowing the NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) ratios is crucial. These ratios directly influence plant growth and nutrient efficiency. Different growth stages require specific nutrient profiles. Applying the correct NPK ratio enhances nutrient utilization while reducing waste.
By conducting soil tests, you can make informed decisions about your fertilizer applications. This practice leads to healthier plants and better yields.
In summary, liquid fertilizers offer numerous benefits for your garden. They enhance nutrient availability and promote quick absorption, leading to healthier plants. You can choose between organic and synthetic options, each with unique advantages. Remember to apply these fertilizers correctly, considering seasonal changes and plant growth stages.
Recent research highlights the importance of balanced nutrient management and the impact of irrigation water on nutrient absorption. For instance, bioorganic fertilizers can improve soil health and support diverse microbial life.
Explore liquid fertilizers as a viable option for soil amendment. They can significantly boost your gardening success!
FAQ
What are liquid fertilizers?
Liquid fertilizers are nutrient solutions that you apply directly to plants or soil. They provide essential nutrients quickly and efficiently, promoting healthy growth and improving soil quality.
How often should I apply liquid fertilizers?
You should apply liquid fertilizers based on your plants’ needs and growth stages. Generally, every 10 to 14 days works well, but adjust according to specific plant requirements.
Can I use liquid fertilizers with other fertilizers?
Yes, you can combine liquid fertilizers with granular fertilizers. This approach allows you to provide immediate nutrients while ensuring long-term soil health. Just monitor application rates to avoid over-fertilization.
Are liquid fertilizers safe for the environment?
Liquid fertilizers can be safe if used correctly. Choose organic options when possible, and follow application guidelines to minimize risks of runoff and pollution.
How do I know if my plants need liquid fertilizers?
Signs of nutrient deficiency include yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and poor fruit development. Conduct soil tests to determine nutrient levels and make informed decisions about fertilizer applications.

