
Propagating Joshua Trees plays a vital role in their conservation. These unique plants face challenges, such as climate change, which has led to their designation as a candidate species under the California Endangered Species Act. You can help by propagating them correctly. There are two primary methods to propagate Joshua Trees: seeds and offsets. Each method offers distinct advantages. By exploring these techniques, you contribute to the survival of this iconic species while enjoying the rewarding experience of growing your own Joshua Trees.
Ecological Benefits:
- Joshua Trees provide food and shelter for various species.
- Their leaves serve as nesting material for birds and small mammals.
- Young leaves are a crucial food source for herbivores during dry seasons.
- A mutualistic relationship with the Yucca moth aids in reproduction and seed dispersal.
Key Takeaways
Choose healthy seeds or offsets for propagation. Healthy materials increase the chances of successful growth.
Provide well-draining soil and ensure adequate sunlight. These conditions are crucial for the health of your Joshua Trees.
Be patient during the germination process. Seeds can take several weeks to sprout, so consistent moisture is key.
Monitor for pests and diseases. Use organic treatments to protect your plants without harming beneficial organisms.
Follow local regulations when propagating. Ensure you comply with conservation laws to protect Joshua Trees.
Propagation Methods

When you decide to propagate Joshua Trees, you have two primary methods to choose from: seed propagation and offset propagation. Each method has its own benefits and challenges. Understanding these methods will help you make informed decisions for successful propagation.
Seed Propagation
Seed propagation involves planting seeds from mature Joshua Trees. This method allows you to grow new trees from scratch. Here are some key points to consider:
Seed Selection: Choose seeds from healthy, mature trees. Healthy seeds have a higher chance of germination and growth.
Germination Process: Seeds require specific conditions to germinate. You should soak them in water for 24 hours before planting. This helps soften the seed coat and encourages sprouting.
Timeframe: Germination can take several weeks. Be patient and provide consistent moisture during this period.
Tip: To improve your chances of success, consider using seeds from different populations. Genetic diversity in Joshua trees is crucial for their adaptation to changing climatic conditions. Some populations may possess genetic variations that support adaptation to warmer and drier environments.
Offset Propagation
Offset propagation is another effective method. This technique involves using offsets, or pups, that grow at the base of mature Joshua Trees. Here’s how to do it:
Identifying Offsets: Look for healthy offsets that are at least a few inches tall. These pups will develop into new trees.
Separation: Carefully separate the offset from the parent tree. Use a clean, sharp tool to avoid damaging the roots.
Planting: Plant the offset in well-draining soil. Joshua Trees thrive in sandy or rocky soils with good drainage. Ensure the new plant receives adequate sunlight and water.
Note: The Western Joshua Tree Conservation Act provides protections for these trees. You must follow local regulations when propagating Joshua Trees. This includes avoiding the removal of healthy trees unless authorized by the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW).
Both methods of propagation require careful attention to detail. Selecting healthy materials is crucial for success. By understanding these propagation methods, you can contribute to the conservation of Joshua Trees while enjoying the process of growing these unique desert plants.
Conditions to Propagate Joshua Trees

To successfully propagate Joshua Trees, you must create the right conditions. These unique desert plants thrive in specific environments. Understanding their soil, light, and temperature needs is essential for successful growth.
Soil Requirements
Joshua Trees prefer well-draining soil. This is crucial because they do not tolerate waterlogged conditions. Here are some optimal soil components and their characteristics:
Soil Component | pH Level | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Coconut coir | Low | Good cation exchange capacity (CEC), retains water, needs buffering with CalMag. |
Pine bark | Low | High CEC, provides aeration, holds less water. |
Horticultural Charcoal | Neutral | Comparable CEC to organics, does not hold much water. |
Kanuma | Low | Regulates pH levels, effective for certain species. |
Lava Rock | N/A | Helps retain water, prevents soil compaction. |
Pumice | N/A | Prevents compaction, adds water retention. |
Peat Moss | Low | Initially good CEC, but compacts over time, choking roots. |
You should aim for a soil mix that allows for good drainage while retaining some moisture. This balance helps your Joshua Trees establish strong roots.
Light and Temperature Needs
Joshua Trees thrive in bright, direct sunlight. They require at least six hours of sunlight daily. Insufficient light can hinder their growth and development.
Temperature also plays a significant role in propagation success. Here’s a summary of ideal temperature ranges for germination:
Temperature (°C) | Germination Rate (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
≥20 | Up to 100% | Best germination rate |
15 | 24% | Lower germination rate |
10 | 0% | No germination |
-11 | Tolerated by leaves | Minimum tolerance |
-25 | Survived by plants | Extreme low tolerance |
59 | Tolerated by leaves | Maximum high tolerance |
51 | Survived by plants | High temperature survival |
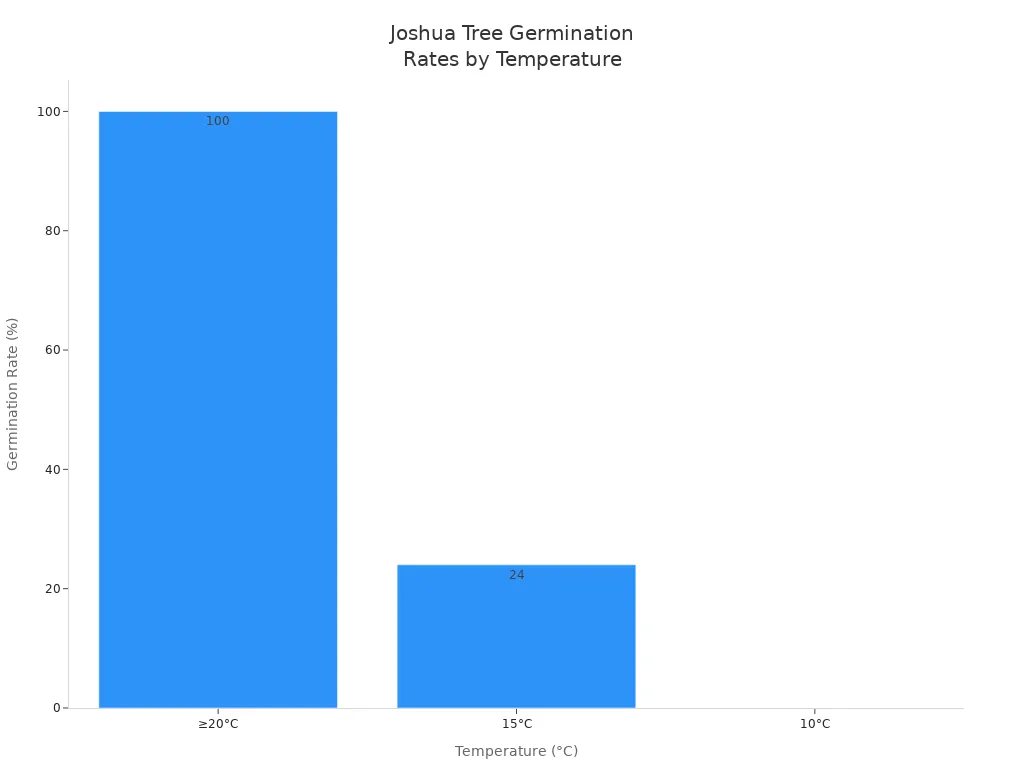
You should aim to keep your propagation area warm, ideally above 20°C, to maximize germination rates. Seasonal temperature fluctuations can impact flowering and seed production, which are vital for propagation. Increased temperatures may enhance flowering, but they can also stress seedlings, making them vulnerable.
By providing the right soil, light, and temperature conditions, you can effectively propagate Joshua Trees and contribute to their conservation.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Seed Propagation Process
To propagate Joshua Trees from seeds, follow these steps:
Prepare the Pot: Fill a 2″-3″ plastic pot with a sterile soil mix that lacks organic components. This ensures good drainage.
Plant the Seeds: Place the Joshua Tree seeds on the surface of the soil. You can start the seeds between damp paper towels before potting them for better results.
Moisten the Soil: Mist the soil until water drains through. Be cautious with watering, as Joshua Trees are sensitive to excess moisture.
Create Humidity: Seal the pot in a plastic bag to maintain humidity. This helps the seeds germinate effectively.
Provide Light: Place the pot in a location with light, avoiding direct sunlight. This prevents overheating.
Monitor Temperature: Keep the temperature above 20°C for optimal germination rates.
Tip: Fresher seeds tend to germinate better than older ones. No pre-treatment like cold stratification or scarification is necessary.
Offset Propagation Process
For offset propagation, follow these steps:
Collect Offsets: Identify healthy offsets at the base of a mature Joshua Tree. Collect them and let them dry in a shaded spot for a day to minimize disease risk.
Prepare the Pots: Plant the dried offsets in pots or trays with drainage holes. Use a suitable succulent potting mix for best results.
Insert the Offsets: Make a small hole in the medium and insert the stalk of the offset. Ensure it is secure.
Provide Sunlight: Place the pots in a safe location with some sunlight to promote healthy growth.
Watering: Water the offsets when the potting mix has completely dried out. Avoid overwatering to prevent root rot.
Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
Watering Technique | Water deeply about every two weeks with 10-20 gallons, ensuring not to rot the trunk or roots. |
Seasonal Watering | After new growth appears, water seasonally for a more natural appearance. |
Secure Planting | Stake the plant securely for the first growing season to prevent movement. |
Soil Amendments | Use soil improved with compost to support growth. |
Avoid Overhead Watering | Do not wet the aboveground parts of the tree, as it can be harmful. |
By following these steps, you can successfully propagate Joshua Trees and contribute to the conservation of these unique desert plants.
Challenges and Solutions
Pests and Diseases
When you propagate Joshua Trees, you may encounter pests and diseases that threaten their growth. Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and scale insects. These pests can weaken your plants and hinder their development. To manage these issues effectively, consider the following solutions:
Organic Treatments: Use neem oil or insecticidal soap to control pests without harming beneficial organisms. These options minimize damage while effectively managing pest populations.
Biological Control: Introduce natural predators like ladybugs to keep pest numbers in check. This method helps maintain a healthy ecosystem around your plants.
Disease Management: Identify specific diseases affecting your trees. Fungal infections often require targeted treatments. Ensure proper watering and drainage to prevent root rot, a common issue for Joshua Trees.
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions significantly impact your success in propagating Joshua Trees. Research shows that warmer and drier conditions lead to lower seedling sprouting and survival rates. Drought and extreme weather events can severely hinder propagation efforts. Here are some strategies to address these challenges:
Watering Practices: Ensure you provide adequate moisture without overwatering. Use a well-draining soil mix to prevent root rot. Water deeply but infrequently to encourage strong root development.
Climate Adaptation: Be aware that climate models predict a drastic reduction in viable Joshua Tree habitat due to rising temperatures and prolonged drought. You may need to adjust your propagation techniques to account for these changes.
Transplant Timing: If you plan to transplant your seedlings, do so during cooler months. This timing helps reduce stress on the young plants and increases their chances of survival.
By understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions, you can successfully propagate Joshua Trees and contribute to their conservation.
Ongoing Care for Joshua Trees
Caring for your newly propagated Joshua Trees is essential for their healthy growth. Proper watering and fertilization will help them thrive in their environment.
Watering and Fertilization
Watering is crucial for the establishment of your Joshua Trees. Follow these guidelines for effective watering:
Ensure the tree is well hydrated before transplanting.
Transplant during the autumn months (October/November) for optimal root recovery.
Provide sufficient follow-up watering to soak the soil down to the root depth (1 to 2 feet).
Water regularly to prevent the soil from becoming bone dry, which is crucial for root development.
For fertilization, consider these options:
Use slow-release fertilizers suitable for desert plants.
Consider mild, slightly acidic organic options like fish emulsion.
Fertilization is not frequent; an annual application or one in late spring and early fall is adequate.
Tip: Some recommend fertilizing with fish emulsion once a year. However, others suggest that this can lead to unnatural growth patterns. The Mojave Cactus Club advises applying a mild, slightly acidic fertilizer in April and October.
Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning helps maintain the health and shape of your Joshua Trees. Here are some best practices:
Tip | Description |
|---|---|
Prune with the Proper Tools | Use appropriate tools for the size and type of limb to avoid damage. Maintain tools for optimal performance. |
Seek Out Diseased or Infected Limbs | Identify and remove any diseased parts to prevent further health issues for the tree. Dispose of them properly. |
Prioritize Safety When Pruning | Use personal protective equipment and avoid unsafe practices like using ladders. Consider hiring professionals for safety. |
Regular maintenance tasks also support healthy growth. Follow this schedule for weeding and mulching:
Maintenance Task | Recommended Timing |
|---|---|
Weeding | Spring and Fall |
Mulching | Spring and Fall |
By following these care tips, you can ensure that your Joshua Trees grow strong and healthy, contributing to their survival in the wild.
In summary, propagating Joshua Trees involves two main methods: seed propagation and offset propagation. You should select healthy seeds or offsets to ensure successful growth. Remember to provide the right soil, light, and temperature conditions.
Be mindful of common mistakes, such as using dull tools or overwatering. These errors can hinder your success. Also, consider the environmental impacts of large-scale propagation projects, including habitat destruction and challenges posed by climate change.
With the right care, you can successfully grow your own Joshua Trees. Try your hand at propagation and share your experiences with others!
FAQ
What is the best time to propagate Joshua Trees?
You should propagate Joshua Trees in spring or early fall. These seasons provide optimal temperatures and moisture levels for successful germination and growth.
How long does it take for Joshua Tree seeds to germinate?
Germination can take several weeks. You must provide consistent moisture and warm temperatures above 20°C to encourage sprouting.
Can I propagate Joshua Trees indoors?
Yes, you can propagate Joshua Trees indoors. Ensure you provide adequate light, warmth, and well-draining soil to support their growth.
How often should I water newly propagated Joshua Trees?
Water newly propagated Joshua Trees when the soil dries out completely. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot.
Are there any pests I should watch for?
Yes, common pests include aphids and spider mites. Regularly inspect your plants and use organic treatments to manage any infestations effectively.

